All the commands here are to be run from terminal (command prompt)
1. Update Linux package management
sudo apt-get update
2. Install C/C++ tools to build native libraries (You might never use them directly, but Ruby gems use them)
sudo apt-get install -y build-essential
3. Install PostgreSQL
a) Install the available version of PostgreSQL in Ubuntu repo (usually not the latest PostgreSQL version)
If you really want to use the latest version of PostgreSQL, use b) Install the latest version
If you are lazy and really don't care about the latest version of PostgreSQL, this should be enough.
sudo apt-get install postgresql postgresql-contrib
If you don't care about the latest version of PostgreSQL,
You can move to the step 4 now.
b) Install the latest version
Install the software-common-properties package
sudo apt-get install -y software-properties-common python-software-properties
Install wget
sudo apt-get install -y wget
See you version of Ubuntu
lsb_release -a
You will see something similar to this:
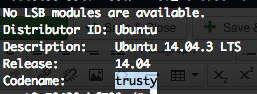
Notice that the Ubuntu code name is trusty. Add PostgreSQL repository to package management system:
sudo add-apt-repository "deb https://apt.postgresql.org/pub/repos/apt trusty-pgdg main"
Or if you don't want to change in the future, use this command:
sudo sh -c 'echo "deb http://apt.postgresql.org/pub/repos/apt/ $(lsb_release -cs)-pgdg main" > /etc/apt/sources.list.d/pgdg.list'
Now import the public key and install:
sudo apt-get install -y --force-yes apt-transport-httpswget --quiet -O - https://postgresql.org/media/keys/ACCC4CF8.asc | sudo apt-key add - sudo apt-get updatesudo apt-get install -y --force-yes postgresql-9.4 pgadmin3
4. Start PostgreSQL the first time
/etc/init.d/postgresql start
When you restart the machine, PostgreSQL will be automatically started.
5. Secure PostgreSQL
Login using command line
sudo -u postgres psql postgres
You will see PostgreSQL command prompt appears:
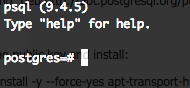
Enter the command:
\password postgres
and give your password when prompted. The password text will be hidden from the console for security purposes.
Type Control+D or \q to exit the posgreSQL prompt.
6. Edit configuration to allow local connection
Open the config file to edit using vim (or gedit, if you don't know how to use vim). Notice that the path after /etc/postgresql contains specific version 9.4 . If you use different version, please modify it accordingly.
sudo vim /etc/postgresql/9.4/main/pg_hba.conf
However, I highly recommend you to spend some time to learn how to use vim.
When the file pg_hba.conf is opened, scroll to the end of the file, and you should see something like this:

Change the "peer" to "md5" and save the file.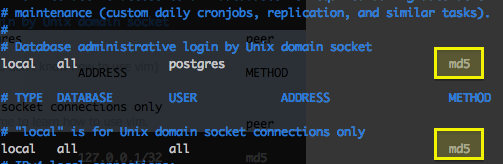
Restart PostgreSQL server:
/etc/init.d/postgresql restart
You are done!
Now your PostgreSQL database is ready to be used in development.
Database username is: postgres
Database password is the password you just set above.
Google about "How to use pgAdmin3 if you are too lazy to use psql command line.
However, if you build Ruby application that reads/writes to PostgreSQL, database operations will be done in Ruby.